16/04/2022
What is ERP software?
ERP stands for “Enterprise Resource Planning,” and it refers to a sort of software or system that allows a company to plan and manage everyday operations including supply chain, production, services, financials, and other processes Accounting and procurement, project management, customer relationship management, risk management, compliance, and supply chain operations are all examples of jobs that may be automated and simplified with ERP Modules.
What Are ERP System Modules?
Each ERP module is specialized for certain corporate operations, providing data and supporting procedures to assist workers in performing their duties. Every module is linked to the ERP system, ensuring that the solution continues to provide a single source of accurate data as the firm expands. The modules are the screwdrivers, wrenches, hammers, and other tools in the ERP system, each with its unique purpose.
How Do ERP Modules Help Businesses?
ERP’s modular architecture allows it to adapt to a company’s changing demands, which is one of the reasons it has grown so popular. Only the modules that are relevant to an organization’s business model, operations, and critical issues can be purchased. As the company grows, it can add ERP modules to handle new demands or issues.
The benefit of modular ERP software is that it allows a business to add capabilities while maintaining the same basis. When requirements change, there is no need to build a new ERP system—a time-consuming process—as long as the firm picks an experienced ERP supplier with a wide range of modules.
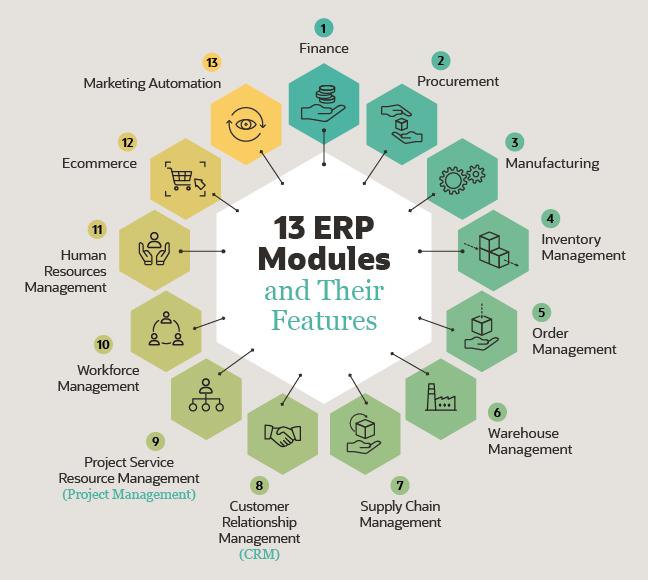
ERP Modules and Their Features:
- Finance: The finance and accounting module is the most significant ERP module since it enables organizations to understand their present financial situation as well as their future prospects. This module’s important features include tracking accounts payable (AP) and accounts receivable (AR), as well as keeping the general ledger. It also creates and maintains critical financial documents including balance sheets, payment receipts, and tax returns. The financial management module may assist the accounting department to close the books on time and in compliance with current revenue recognition requirements by automating operations like billing, vendor payments, cash management, and account reconciliation. It also contains the information required for financial planning and analysis staff to generate essential reports, such as profit and loss (P&L) statements and board reports, as well as run scenario plans.
- Procurement: The procurement module, often known as the purchasing module, helps an organization get the resources or products it needs to manufacture and/or sell goods. This module allows companies to establish a list of approved vendors and link those vendors to specific goods, assisting with supplier relationship management. The module may automate quotation requests and then track and analyze the responses. The procurement module assists the buying department in preparing and sending out purchase orders when a firm accepts a bid. It may then follow the purchase order as the vendor converts it to a sales order and sends the products, adjusting inventory levels automatically when the order arrives.
- Manufacturing: MRP systems, the earliest type of ERP, were designed with manufacturers in mind, and manufacturing remains a significant component of ERP today. In today’s ERP systems, production management or manufacturing execution system is usually included (MES). The manufacturing module assists firms in planning production and ensuring that they have all they require for scheduled production runs, such as raw materials and machinery capacity. It may update the status of goods-in-progress and assist organizations in tracking actual output against predicted output during the manufacturing process. It also captures information on products in progress and finished goods in real-time, providing a real-time image of the shop floor. It can figure out how long it takes to make an item on average, then compare supply to predicted demand to figure out how much to make.
- Inventory Management: Inventory control is enabled through the inventory management module, which tracks item quantities and locations down to individual SKUs. Through a connection with the procurement tool, this module provides a full view of not only present but also incoming inventories. This piece of software aids in the management of inventory expenses, ensuring that organizations have enough stock without tying up too much cash in inventory. An inventory management tool may compare sales patterns to available inventory, allowing businesses to make more educated decisions that raise profits and inventory turnover (a measure of how often inventory is sold over a certain period). Purchase orders, sales orders, and shipments may all be handled using the inventory management application for businesses that don’t have additional supply chain management modules. A version of this technology that can track inventories across several sites will be required by larger enterprises.
- Management of Orders: An order management module maintains track of orders from reception through delivery. Consumer orders are routed to the warehouse, distribution center, or retail shop, where they are processed, fulfilled, and dispatched to the customer. The order management module keeps customers happy and reduces expedited shipping costs by preventing orders from going missing and increasing on-time delivery rates. More complicated order management solutions can help a company determine the most cost-effective option for processing an order based on available inventory and the buyer’s location—a store vs. a warehouse vs. a third-party fulfillment partner.
- Warehouse Management: For organizations that operate their own warehouses, a warehouse management module may provide a quick return on investment. Based on the configuration of the facility, this program can efficiently lead warehouse staff through all warehouse activities, from put away when items arrive through picking, packaging, and shipping. It can also assist businesses in scheduling workers depending on predicted order volume. Depending on which picking strategy is most effective for a certain firm, the warehouse management module can enable batch picking, wave picking, and zone picking, and some modules can display staff the most efficient pick path. Employees can quickly discover the proper goods and get shipments out the door when the warehouse management module is coupled with inventory management and order management software.
- Supply Chain Management: From sub-suppliers to suppliers to manufacturers to distributors to retailers or customers, a supply chain management module records each step in the movement of materials and items along the supply chain. It can also take care of any materials or items that have been returned for a refund or replacement. Supply chain management, as previously said, may encompass a wide range of modules such as procurement, inventory management, production, order management, and warehouse management. It may, however, have capabilities beyond those modules’ primary capabilities.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): The customer relationship management (CRM) module stores all client and prospect information. This comprises both a person’s purchasing history and the company’s communication history with them—for example, the date and time of calls and emails. When engaging with a customer, a CRM enhances customer service by allowing employees to quickly access all of the information they require. CRM is also used by many firms to handle sales leads and prospects. It may keep track of prospects’ communications and recommend which consumers should be targeted for certain promotions or cross-sell possibilities. Customer segmentation (allowing for more focused marketing) and advanced contact management and reporting tools may be included in more powerful CRM systems.
- Professional Services Automation (Service Resource Management): A company can plan and manage projects using professional services automation (PSA) module, often known as a service resource management module. This module is frequently used by service-based enterprises. The tool keeps track of project progress while also managing human and capital resources and allowing managers to approve costs and timesheets It facilitates team communication by centralizing all connected documents.. In addition, the PSA module may compile and send bills to clients automatically depending on billing cycle parameters.
- Workforce Management: A workforce management module is similar to a human resource management module, except it is designed for companies that have more hourly employees than salaried employees. It can keep track of employee hours and attendance, as well as productivity and absenteeism. Payroll may or may not be included in the workforce management module. A payroll sub-module delivers payments on a fixed schedule to workers, deducting the relevant taxes and handling cost reimbursement. It may also provide reports on payroll costs, total overtime hours, and other key performance indicators.
- Human Resources Management: A human resource management (HRM) or human capital management (HCM) module normally includes all of the functions of a workforce management program as well as some extra features. HRM may be compared to customer relationship management for employees. This popular module maintains documents like as performance reports, job descriptions, and offer letters, as well as thorough information on all personnel. It keeps track of not only hours worked, but also paid time off (PTO), sick days, and perks. The HRM module avoids a lot of redundant or erroneous data that many firms save in separate spreadsheets since it stores a lot of information on every employee across the organization.
- E-commerce: For firms that wish to sell online, several ERP suppliers include an e-commerce module. This module enables companies to quickly set up an ecommerce website for business-to-business (B2B) or business-to-consumer (B2C) transactions. User-friendly capabilities in leading commerce solutions make it simple for employees to add new things, alter product material (descriptions, names, specifications, photos, and so on), and modify the style and feel of the website. When the ecommerce application is connected with other ERP programs, the ecommerce module feeds all payment, order, and inventory information into a common database. This guarantees that all transactions are recorded in the accounting system that out-of-stock goods are removed from the website, and that orders are delivered on time.
- Marketing Automation: A marketing automation module has been developed by several software companies, similar to e-commerce. Marketing campaigns are managed through digital channels such as email, online, social media, and SMS using a marketing module. It includes extensive customer segmentation tools, so consumers only receive relevant communications, and it can automate email sends depending on campaign guidelines. Marketing automation software, whether integrated into an ERP system or purchased separately, may generate precise information on campaign effectiveness, allowing marketers to better plan and budget for future efforts. These apps boost lead generation, client retention, and revenue over time.
Invest in best ERP for your business to gain consistent growth and development. Infusion ERP is one the best ERP that only provides all the features but also helps you to decide with its free trial version. So if you want your business process to run effectively and efficiently, consider Infusion ERP!
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
- Mark on ERP Software
Categories
Completely synergize resource is taxing relationships via premier are man niche markets. Professionally cultivate one to one customer.


